Not sure where to begin with your invention design?
Get FREE Info NOW!
Resource Articles
How to Get a Prototype Made
By MarketBlast
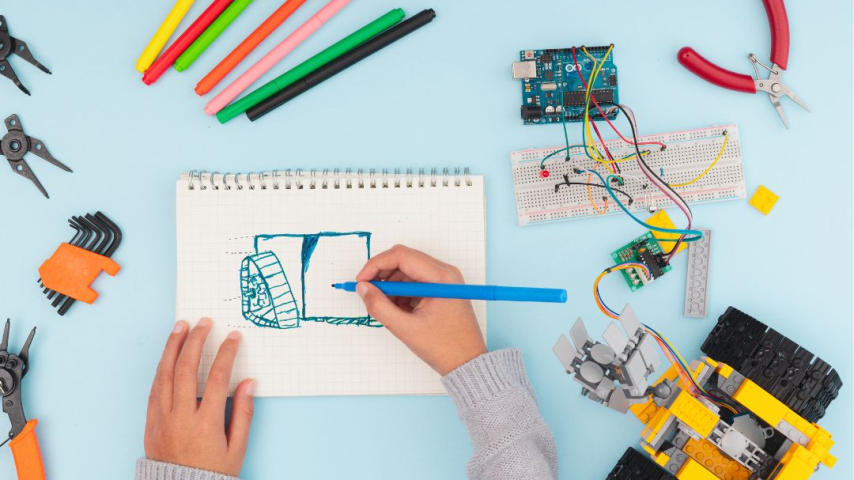
Not sure where to begin with your invention design?
Get FREE Info NOW!
Why
Prototyping is Key for Inventors
Every
invention begins as an idea, but to transform that idea into a viable product,
you need more than just a mental image or a drawing on paper—you need a
prototype. Prototyping allows you to see how your invention will look and
function in the real world. It's a process that offers clarity, fosters
creativity, and can highlight the potential flaws or areas for improvement in
your design.
The
question most inventors face is: how do you actually get a prototype made?
Whether you’re a first-time inventor or a seasoned creator, understanding the
steps and strategies for prototyping can make the difference between a concept
that remains on the drawing board and a product that succeeds in the market. In
this article, we’ll walk you through the entire process of getting a prototype
made, from brainstorming and design to materials, costs, and finding the right
professionals to bring your invention to life.
Why
a Prototype Is Important
Before
diving into the "how," let’s clarify why having a prototype is so
essential:
Proof
of Concept
A prototype demonstrates that your
idea works. It’s a tangible representation that proves your invention can
function as intended. This can help you make adjustments, solve unforeseen
problems, and refine your design before it reaches the manufacturing stage.
Patent
and Legal Protection
Prototypes are often needed to support
your patent application. They can serve as proof that your invention is viable
and unique, which can strengthen your claim when applying for a patent.
Investor
and Manufacturer Attraction
If you want to attract investors or
manufacturers, a prototype is invaluable. Being able to show a potential
partner what your product looks like and how it works will increase their
confidence in your project. It turns your idea into something they can see,
touch, and test.
Market
Feedback
A prototype allows you to test your
invention in the real world. You can use it to gather feedback from potential
customers or focus groups, helping you make changes and improvements that align
with market needs before full production.
Steps
to Get a Prototype Made
The
prototyping process might feel overwhelming, but breaking it down into
manageable steps makes it more accessible. Let’s explore each of these steps in
detail.
Define
Your Objective
Before
you start building your prototype, you need to clearly define what you want to
achieve with it. Are you looking to create a simple proof of concept to test
functionality, or do you need a working model that closely resembles the final
product?
There
are different types of prototypes, including:
- Concept
Prototypes: These are basic
models that demonstrate the core functionality of your idea without focusing on
design or materials.
- Working
Prototypes: These models not
only show the design but also simulate the actual function of the product.
- Final
Prototypes: The final
versions are usually fully functional and made from materials that closely
resemble the final product.
Knowing
your goal will help guide the materials, time, and resources needed for the
prototype.
Sketch
and Design Your Prototype
The
first step in creating a physical version of your idea is to sketch it out. You
don’t have to be a professional artist—just draw your invention from different
angles and highlight its key features. Focus on how the different components
will work together. Include measurements, materials, and any functional details
that will help you (and eventually, a professional) bring the prototype to
life.
Once
you’ve created a rough sketch, you may want to move to a digital design tool
for greater precision. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software is commonly used
for this step. CAD allows you to create a 3D model of your invention, which can
be used later for advanced prototyping techniques such as 3D printing or
machining. If you’re unfamiliar with CAD software, you might want to hire a
freelance designer or a prototyping company to assist you.
Popular
tools and software for design include:
- Fusion 360
- SolidWorks
- AutoCAD
- Tinkercad (for beginners)
Choose
the Right Materials
The
materials you choose for your prototype will depend on the complexity of your
invention, your budget, and the prototype’s intended purpose. If you’re
building a simple proof of concept, you may be able to use inexpensive
materials like cardboard, plastic, or even household items. If you need a more
advanced prototype, you may require specialized materials such as metal,
high-grade plastics, or electronics.
Considerations
when selecting materials:
- Durability: Will the prototype need to be tested multiple
times or withstand certain conditions (heat, pressure, etc.)?
- Functionality: Does your invention require specific parts to
be flexible, sturdy, or conductive?
- Cost: Some materials are expensive, especially for early-stage prototyping, so it’s important to find a balance between quality and cost-efficiency.
Not sure where to begin with your invention design?
Get FREE Info NOW!
Build
a Proof of Concept
At
this stage, you’ll create your first version of the prototype. For many
inventors, this will be a basic proof of concept designed to test the core
functionality of the idea. Depending on the complexity, you can try building
the prototype yourself or hire a professional.
DIY
Prototyping
For
simple inventions, many inventors choose to build their first prototype
themselves. This can be done using affordable tools like:
- 3D
printers: Many hobbyists and small businesses
have adopted 3D printing as an efficient and cost-effective way to create
prototypes.
- Moldable
plastics: Products like Sugru or InstaMorph
allow inventors to easily create or alter parts.
- Electronics
kits: For inventions involving circuits or
sensors, kits like Arduino or Raspberry Pi can be invaluable for DIY
electronics.
DIY
prototyping is cost-effective and gives you a hands-on understanding of how
your invention works. However, it may not be suitable for more complex
products.
Professional
Prototyping Services
For
more advanced prototypes, you may need to hire a professional or use a
prototyping service. These professionals can take your design and create a
working model using techniques like machining, laser cutting, or injection
molding. Many companies specialize in helping inventors bring their prototypes
to life.
Prototyping
firms typically offer services like:
3D
printing for precise, detailed models
Machining
for durable parts, especially metal
Injection
molding for parts that need to be manufactured in larger quantities
Some
companies that specialize in prototyping include:
- ProtoLabs
- Fictiv
- Xometry
- 3D Hubs
Test
and Refine the Prototype
Once
you have a working prototype, it’s time to test it rigorously. Here are the key
things to focus on during the testing phase:
- Functionality: Does it work as intended? Are there any
design flaws?
- User
Experience: Is it easy to
use? Does it fulfill the need it’s designed to solve?
- Durability: How well does it hold up under stress or
extended use?
Based
on the testing results, you will likely need to make adjustments. The
prototyping process is often iterative, meaning you’ll go through several
rounds of testing and refinement before arriving at a final version.
Create
a Final, Production-Ready Prototype
After
refining your design, the next step is to create a final prototype that is
ready for production. This version should be nearly identical to the product
you intend to manufacture and sell. It should be built using the same materials
and methods that will be used in mass production.
At
this stage, you might also start considering manufacturing costs, supplier
sourcing, and the logistics of bringing your product to market.
Costs
and Timeline for Prototyping
The
cost of getting a prototype made varies widely depending on the complexity of
the invention and the type of materials used. Here’s a rough breakdown of what
to expect:
Basic
DIY Prototype: $100 – $500
3D
Printed Prototype: $300 – $5,000
Machined
Prototype: $1,000 – $10,000+
Injection
Molded Prototype: $5,000 – $50,000+
The
timeline for creating a prototype can also vary. A simple DIY prototype might
only take a few days or weeks, while a more complex, professional prototype can
take several months to complete.
Working
with Prototyping Companies: What to Look For
When
selecting a prototyping company or service, there are a few key factors to
consider:
Experience: Look for companies with experience in your
industry or with products similar to yours.
Capabilities: Ensure they offer the specific services you
need, such as 3D printing, machining, or electronics.
Cost
Transparency: Ask for clear
estimates and understand what is included in their pricing.
Communication: A company that communicates well and
understands your vision will save you time and frustration.
Quality: Ask to see examples of their previous work to
ensure the quality of their prototypes meets your expectations.
Some
Final Thoughts: From Idea to Reality
Creating
a prototype is an exciting and vital step in the invention process. It takes
your idea from the theoretical stage and turns it into something you can see,
touch, and test. Whether you opt for a DIY approach or hire a professional
prototyping firm, knowing how to get a prototype made can significantly
increase your chances of success in bringing your product to market.
By
following the steps outlined in this guide—defining your objective, designing a
model, choosing materials, testing, refining, and creating a final
prototype—you’ll be well on your way to transforming your invention into a
reality.
Not sure where to begin with your invention design?
Get FREE Info NOW!
Founded with the vision to transform the
landscape for monetizing and commercializing innovative products and brands,
MarketBlast® is the leading Product Hunt and Submission Management Platform
connecting buyers and sellers across the globe. Since our inception, we have
been dedicated to empowering small companies, startups, entrepreneurs and
emerging brands to connect directly with industry companies and accelerate
their own marketing and sales efforts to achieve lasting results.
At MarketBlast®, we believe
that innovation thrives on collaboration. Our platform provides seamless access
to a diverse network of companies, proprietary content marketing and
advertising programs, and access to a wide range of resources designed to
support the overall journey toward success.
For more information on signing up for a
premium membership or to start a content marketing campaign for your products,
email info@marketblast.com or
visit www.marketblast.com.
Other
Related Articles
How Do You Get
a Prototype of Your Invention Made?
Do You Need an
Invention Prototype?
How Much Does
It Cost to Design a Logo?
Can Developing
a Prototype for Your Invention Help You Succeed
Do You need a
Prototype for Your Invention