- Bring Your Idea to Life -
Get Your Free Product Design Info Today!
Resource Articles
Product Design and Prototyping
By MarketBlast
- Bring Your Idea to Life -
Get Your Free Product Design Info Today!
The
Bridge Between Concept and Reality
In
the world of product development, the path from an idea to a market-ready
product is filled with challenges, revisions, and breakthroughs. Product design
and prototyping are two critical steps in this journey. They allow creators to
breathe life into their concepts, transforming them into tangible products that
can be tested, refined, and eventually produced on a larger scale. These stages
are essential to building products that function as intended and are attractive
to consumers and feasible to manufacture.
Whether
you're an inventor, entrepreneur, or designer, mastering product design and
prototyping can significantly improve your product's chances of succeeding in
the marketplace. In this article, we'll explore the complete process, from
initial ideation to creating the first working prototype. We will provide
insights, tips, and best practices to guide your development journey.
What
Is Product Design?
Product
design is the process of conceptualizing and creating a product that solves a
particular problem or fulfills a specific need. It combines creativity,
engineering, and practicality, where aesthetics and functionality must
harmonize. Product design involves how the product looks and how it works,
feels, and interacts with the user.
Key
Aspects of Product Design:
User-Centered
Design
Every
successful product design process starts with the end-user in mind. Designers
must understand their target audience's needs, behaviors, and pain points to
create functional and appealing products. User-centered design ensures that the
product solves real problems and is intuitive.
Functionality
A
product must efficiently fulfill its primary purpose. Whether it's a consumer
gadget or a piece of industrial machinery, the design must prioritize function
over form without sacrificing ease of use. Designers need to think about how
the product will be used, how its features will work, and how it will perform
under real-world conditions.
Aesthetic
Appeal
A
product's design also plays a significant role in attracting customers. The way
a product looks—its shape, color, and texture—can be a powerful differentiator
in a crowded marketplace. While aesthetic elements should never overshadow
functionality, a visually appealing product will have a stronger presence on
store shelves and in customers' minds.
Feasibility
and Cost
Beyond
functionality and aesthetics, product design must also consider the
practicality of manufacturing. Designers must know the costs associated with
production materials, manufacturing processes, and distribution. A great design
is worthless if it's too expensive or complex to produce at scale.
The
Process of Product Design
Product
design is an iterative process that begins with a simple idea and evolves into
a detailed plan for a real-world product. Here's how the process typically
unfolds:
1.
Ideation and Concept Development
The
first step in product design is ideation, where the product concept is born.
Ideation is the process of brainstorming and generating ideas based on a
problem that needs solving or a market opportunity. During this phase,
exploring a wide range of possibilities without limitations is important,
encouraging creativity and innovation.
Once
several ideas have been generated, the next step is refining them into a
workable concept. This involves selecting the most promising ideas and
developing them further into rough sketches or simple diagrams. These concepts
can be discussed with key stakeholders, partners, or potential customers to
gather feedback and refine the direction.
2.
Market Research and Validation
After
a concept has been developed, market research is essential. This step involves
analyzing the target market, understanding competitor products, and gauging
consumer interest. Research tools like surveys, focus groups, and interviews
with potential users can provide valuable insights into whether the product
will be in demand and what features are most important.
Market
research helps you determine whether your product concept is viable. It can
also reveal gaps in the market that you can exploit to differentiate your
product from the competition.
3.
Sketching and Initial Design
Once
the concept has been validated through market research, designers move into the
sketching phase. This is where rough drawings are created to outline the
product's basic structure, form, and functionality. The goal is to capture the
product's essence without delving too deeply into technical details.
These
early sketches are meant to be exploratory and flexible. Designers may create
several versions to test different approaches and gather feedback. It's also an
excellent opportunity to experiment with the product's shape, size, and
ergonomic considerations.
4.
Digital Design (CAD)
After
the initial sketches are approved, the next step is to translate these concepts
into more detailed digital designs using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software.
CAD programs, such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, or Fusion 360, allow designers to
create precise 3D models of the product. These models enable engineers and
designers to visualize the product from all angles, simulate functionality, and
even calculate measurements for production.
Digital
designs also make it easier to test the product's functionality before creating
a physical prototype. Designers can run simulations to ensure all parts work
together seamlessly and avoid costly errors down the road.
5.
Design for Manufacturing
Designing
a product is only half the battle. The next challenge is ensuring that the
design can be manufactured efficiently and affordably. This is known as Design
for Manufacturing (DFM). During this stage, designers work with engineers and
manufacturers to adjust the product's design to suit large-scale production.
Factors
to consider during DFM include:
Material
Selection: Choosing cost-effective, durable, and
suitable materials for the product's intended use.
Manufacturing
Processes: Ensuring that the design can be
produced using standard manufacturing methods (e.g., injection molding, 3D
printing, CNC machining).
Assembly: Simplifying the product's design to reduce
the number of parts and streamline the assembly process.
- Bring Your Idea to Life -
Get Your Free Product Design Info Today!
What
Is Prototyping?
Prototyping
is the process of building an early version or sample of the product to test
its design, functionality, and overall performance. It bridges the conceptual
design phase and the final product launch, allowing designers, engineers, and
stakeholders to evaluate how the product performs in real-world conditions.
Types
of Prototypes
There
are several types of prototypes, each serving a specific purpose at different
stages of product development:
Proof
of Concept Prototype
A
proof-of-concept (PoC) prototype is a basic model that demonstrates the core
idea behind the product. This early prototype may not include all the features
or aesthetic details of the final product, but it proves that the concept
works. PoC prototypes are often created using simple materials like cardboard,
foam, or even 3D-printed components.
Working
Prototype
A
working prototype is a more advanced version that closely resembles the final
product's appearance and functionality. This type of prototype is used to test
how the product performs under real-world conditions. It includes all the
necessary features and components and is typically made from materials that
will be used in the final version.
Visual
Prototype
A
visual prototype focuses on the product's appearance rather than functionality.
It presents the product to stakeholders, investors, or potential customers,
showing how it will look. While it may not function, a visual prototype is
essential for gathering feedback on aesthetics and design.
Final
Prototype
The
final prototype is essentially a fully realized version of the product,
combining both functionality and aesthetics. It's the last iteration before
mass production and is used to ensure that the product meets all design,
performance, and manufacturing requirements.
The
Importance of Prototyping
Prototyping
is a crucial part of product development for several reasons:
Testing
and Refining the Design
Prototyping
allows designers to test their concepts in the real world. By building physical
models, they can see how the product functions, identify design flaws, and make
improvements. It's a chance to test everything from usability to durability
before moving into full-scale production.
Reducing
Risk
Building
a prototype reduces the risk of costly mistakes during production. By catching
issues early, you avoid expensive reworks and redesigns once manufacturing has
begun. Prototyping ensures the product is well-tested and ready for the
market's demands.
Gathering
Feedback
Prototypes
are also essential for gathering user feedback. Allowing potential customers,
investors, or stakeholders to interact with the product provides valuable
insights into its usability and appeal. This feedback can help you refine the
product before launch, ensuring it meets customer expectations.
Demonstrating
Feasibility to Stakeholders
A
functional prototype is a powerful tool when seeking investment or approval
from stakeholders. It shows that the concept is viable and close to production,
giving investors confidence in the product's potential.
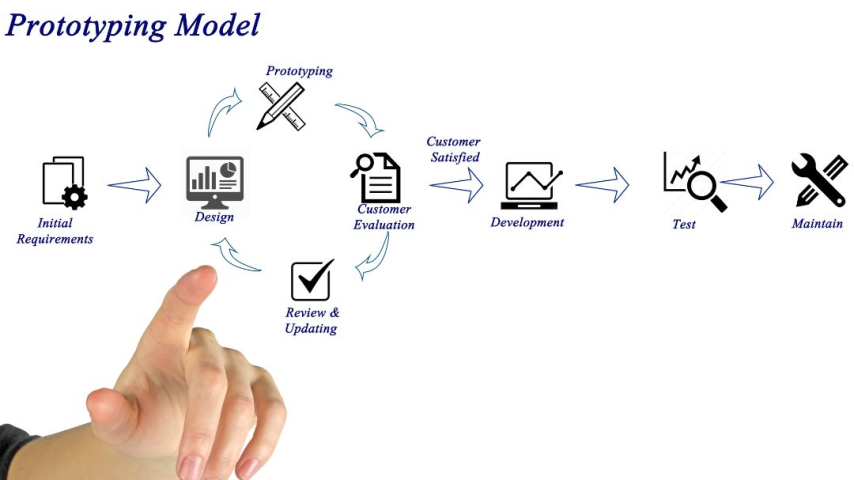
The
Prototyping Process
The
prototyping process typically follows several stages, each offering
opportunities to test and refine the product:
Build
an Initial Prototype
The
first step is creating an initial prototype, often a simple proof of concept.
This prototype helps designers and engineers test the product's basic
functionality and identify any major design flaws.
Test
and Gather Feedback
After
building the prototype, thorough testing is essential. This may involve user
testing, stress testing, and functionality testing to ensure the product
performs as expected.
Iterate
and Improve
The
product design may need to be modified based on feedback from testing.
Prototyping is an iterative process, meaning several rounds of revisions may be
necessary before the product is ready for production.
Build
the Final Prototype
Once
all issues have been addressed, the final prototype is built. This version
should be identical to the product that will be manufactured, both in
appearance and function.
Moving
from Prototyping to Production
Once
the final prototype has been approved, the product is ready for production. At
this stage, it's essential to work closely with manufacturers to ensure the
design is scalable and cost-effective. Design for Manufacturing principles come
into play here, helping to streamline production and reduce costs.
Final
Thoughts About Bringing Ideas to Life
Product
design and prototyping are at the heart of successful product development.
Together, these processes transform abstract concepts into tangible products,
ensuring that each detail—whether functional, aesthetic, or practical—has been
thoroughly tested and refined. By following a structured approach to design and
prototyping, inventors and businesses can reduce risks, maximize market
potential, and deliver products that stand out from the competition. Whether
you're at the ideation stage or building your first prototype, mastering these
steps will help bring your ideas to life.
- Bring Your Idea to Life -
Get Your Free Product Design Info Today!
Founded with the vision to transform the
landscape for monetizing and commercializing innovative products and brands,
MarketBlast® is the leading Product Hunt and Submission Management Platform
connecting buyers and sellers across the globe. Since our inception, we have
been dedicated to empowering small companies, startups, entrepreneurs and
emerging brands to connect directly with industry companies and accelerate
their own marketing and sales efforts to achieve lasting results.
At MarketBlast®, we believe
that innovation thrives on collaboration. Our platform provides seamless access
to a diverse network of companies, proprietary content marketing and
advertising programs, and access to a wide range of resources designed to
support the overall journey toward success.
For more information on signing up for a
premium membership or to start a content marketing campaign for your products,
email info@marketblast.com or
visit www.marketblast.com.
Other
Related Articles
How Do You Get
a Prototype of Your Invention Made?
Do You Need an
Invention Prototype?
How Much Does
It Cost to Design a Logo?
Can Developing
a Prototype for Your Invention Help You Succeed
Do You need a
Prototype for Your Invention